Federal Reserve Maintains Rates Amid Global Economic Context
The Federal Reserve keeps interest rates steady, signaling potential cuts later this year, as global economic outlooks shift with various central bank decisions.
Overview
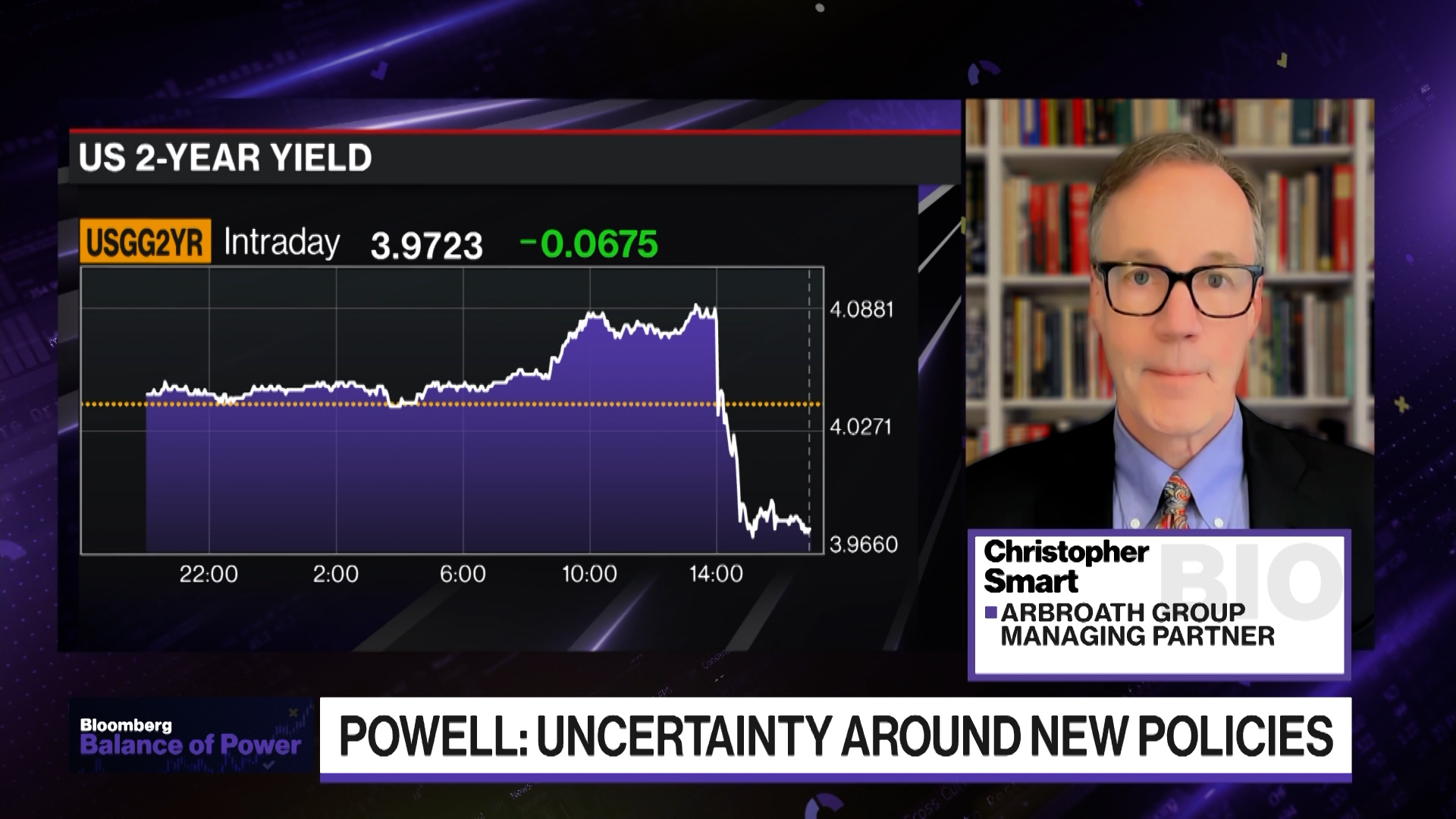
The Federal Reserve has opted to maintain interest rates at 4.25%-4.5%, with Chair Jerome Powell suggesting potential cuts amid rising inflation and economic uncertainty. The decision has been positively received, contributing to a stock market rally, with the S&P 500 up 1.1%. This follows a similar stance from the Bank of England, expected to hold its rates at 4.5% next week amidst concerns over inflation and economic slowdown. Analysts predict two further cuts for the Bank of England by year-end. Meanwhile, China's central bank held its lending rates steady, balancing growth efforts against trade frictions.
Report issue

Read both sides in 5 minutes each day
Analysis
- The Federal Reserve has decided to maintain its interest rates at a range of 4.25% to 4.5% while expressing concerns about rising inflation and slower economic growth due to the effects of President Trump’s tariff policies.
- Recent projections from the Fed show an anticipated inflation rate of 2.8% for this year, up from a previous estimate of 2.5%, signaling increased uncertainty in the economic outlook.
- Fed Chair Jerome Powell has highlighted the significant role of tariffs in driving inflation and emphasized the importance of a cautious approach in policy-making given the high levels of uncertainty surrounding recent economic changes.
Articles (49)
Center (38)
FAQ
The Federal Reserve maintained interest rates due to economic uncertainty, solid labor market conditions, and elevated inflation. Despite these factors, they signaled potential future rate cuts as economic growth slows and inflation persists above target[1].
The decision to hold interest rates steady and signal potential future cuts led to a positive stock market response, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average rising significantly following the announcement[4].
Similar to the Federal Reserve, the Bank of England is expected to hold its rates steady, with predictions of two cuts by year-end. China's central bank also maintained its lending rates, balancing growth efforts against trade frictions[5].
The Federal Reserve is considering factors such as inflation persistence, economic growth slowdown, labor market conditions, and the impact of tariffs on inflation. These factors will guide future rate adjustments.
History
- 7M

 4 articles
4 articles
- 7M

 4 articles
4 articles
- 7M

 3 articles
3 articles
- 8M

 3 articles
3 articles